Fact Sheets
Fact Sheets
CALCULATING YOUR SHIPMENTS’ CHARGEABLE WEIGHT - CUBIC METRE VOLUME (CBM)
Freight shipment cubic volumes are typically required to get a price quote. Use this CBM calculator to calculate CBM and also to calculate how many products fit in a shipping container.
CBM is also critical for calculating dimensional weight, chargeable weight, calculating freight class, or for requesting a freight quote.
What is the meaning of CBM?
CBM, or cubic meter, is the freight volume of the shipment for domestic and international freight. CBM measurement is calculated by multiplying the width, height and length together of the shipment.
The CBM formula is a simple calculation – it’s the product of the quantity of items * length * width * height. If your shipment has different sized items, simply repeat the formula for each size and add up the volumes.
Chargeable Weight:
To compare the real weight versus the volumetric weight, remember that the carrier will charge you for the higher of the two:
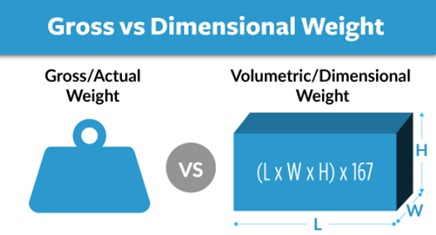
Volumetric Weight
Airfreight, Road transportation and courier services are charged per kilo by the carrier (airlines and trucking companies). However, goods in relation to their weight can occupy a lot of space and so the charge can be for the volumetric weight
For example, for an airfreight shipment:
The volume ratio used is 1:6 for airfreight so:
1 Cubic metre (1 m3) = 166.66 KG
This means that 167kg is equal to or greater than 1 cubic metre (1 M3)
Chargeable Weight
So, to get to the chargeable weight of your shipment - which is what you will pay for - the carrier will check to see which is higher: the ACTUAL WEIGHT or the VOLUMETRIC WEIGHT.
Container Dimensions – what type and size do you need?
There are a variety of different types and sizes of sea containers. Find out more about the types and sizes of containers (and their dimensions).
Whether you have a full container load (FCL) or less than a container load (LCL) , we will be able to provide you with the container you need for your shipment.
Check out this useful guide below, provided by our global logistics partners at DSV to learn more:
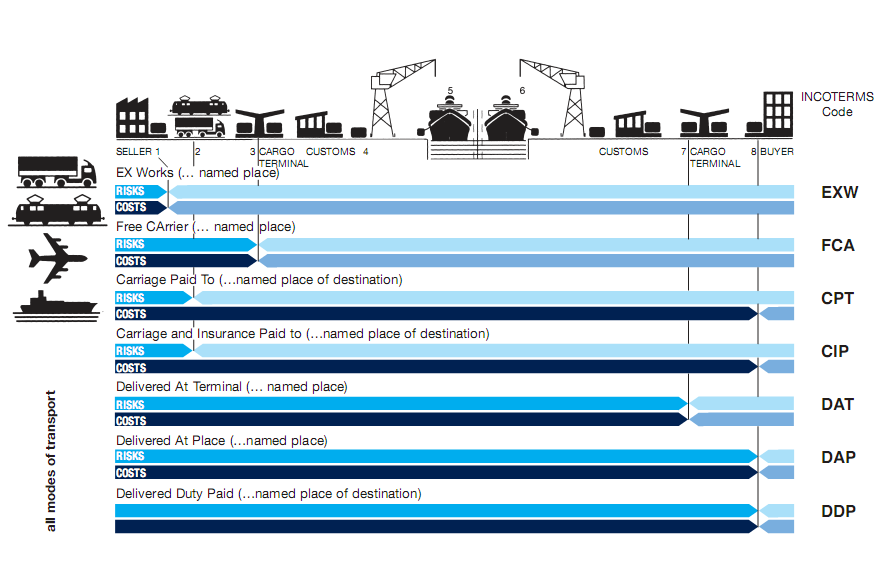
1. INCOTERMS 2020
What are Incoterms® rules?
The Incoterms® rules are the world’s essential terms of trade for the sale of goods. Whether you are filing a purchase order, packaging and labelling a shipment for freight transport, or preparing a certificate of origin at a port, the Incoterms® rules are there to guide you. The Incoterms® rules provide specific guidance to individuals participating in the import and export of global trade on a daily basis.
INCOTERMS ® were developed by the International Chamber of Commerce, Paris, France in 1936 and are regularly updated to reflect changes in transportation and documentation. The current version is Incoterms ® 2020
The below guide is published by FAMS and is for illustrative purposes only and is not sponsored or endorsed by the ICC.
FINDING HS CODES
HOW TO FIND THE CORRECT HTS TARIFF CLASSIFICATION BY USING FIND HS CODES.
The Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System" developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO) is universally used for the classification of products. The system, generally referred to as "Harmonized System" is a multipurpose international product nomenclature. It comprises around 5,000 commodity groups; each identified by a six digit code, arranged in a legal and logical structure and is supported by well-defined rules to achieve uniform classification. Over 98% of the merchandise in international trade is classified in terms of the "HS Code" or "HTS Code" which is used by more than 200 countries as a basis for their customs tariffs and for the collection of international trade statistics. This means that the six digit code mentioned above, refers to the same good in the customs of almost all countries in the world. Hence, the "Harmonized System" provides a common ground and universal economic language for international trade.
Determining the correct HS Code has a crucial importance for trade professionals mainly for two reasons:
- For importers/exporters correct classification is a legal responsibility, as it is the basis for critical implementations such as the customs duty and trade measures that apply, import-export admissibility of the related product, etc. Therefore misclassification of a product, may have damaging consequences for a company (e.g. losing money, being subject to penalties or worse).
- Tariff classification codes (i.e. HS Codes) are extensively used by trade professionals to learn and analyse crucial trade information such as trade measures effective on certain goods, trade statistics, price monitoring, etc.